Your centralized product development hub in Notion
Stay on top of your work without the back-and-forth. Notion brings together your team's docs, tasks, and communications in one collaborative space — where work flows naturally.
- 1. Strategize with a customizable product roadmap
- Create a roadmap database
- View product roadmap in different ways
- Work inside your roadmap
- 2. Manage granular engineering tasks
- Bring work happening elsewhere into Notion
- 3. Use customer feedback to inform your work
- 4. Connect all aspects of product development
Many product teams use one tool for roadmaps, another for customer feedback, and yet another for tasks.
This creates a fragmented picture of what’s happening, and you waste time chasing for updates or searching for information. Teams can go off track and miss key insights to make the product better.
Instead of switching between several apps, you can manage everything, from roadmaps and engineering tasks to meeting notes, wikis, and documents in Notion, saving time and making collaboration effortless.
Bring product managers, engineers, designers, and everyone else onto the same page with clear goals, priorities, and timelines, to help you stay organized, work efficiently, and ship faster.
A roadmap is a living plan that connects to company goals, documentation, tasks, and more.
Teams using Notion can share one product roadmap that guides them through the product development cycle.
Here’s how to create a product roadmap in Notion.
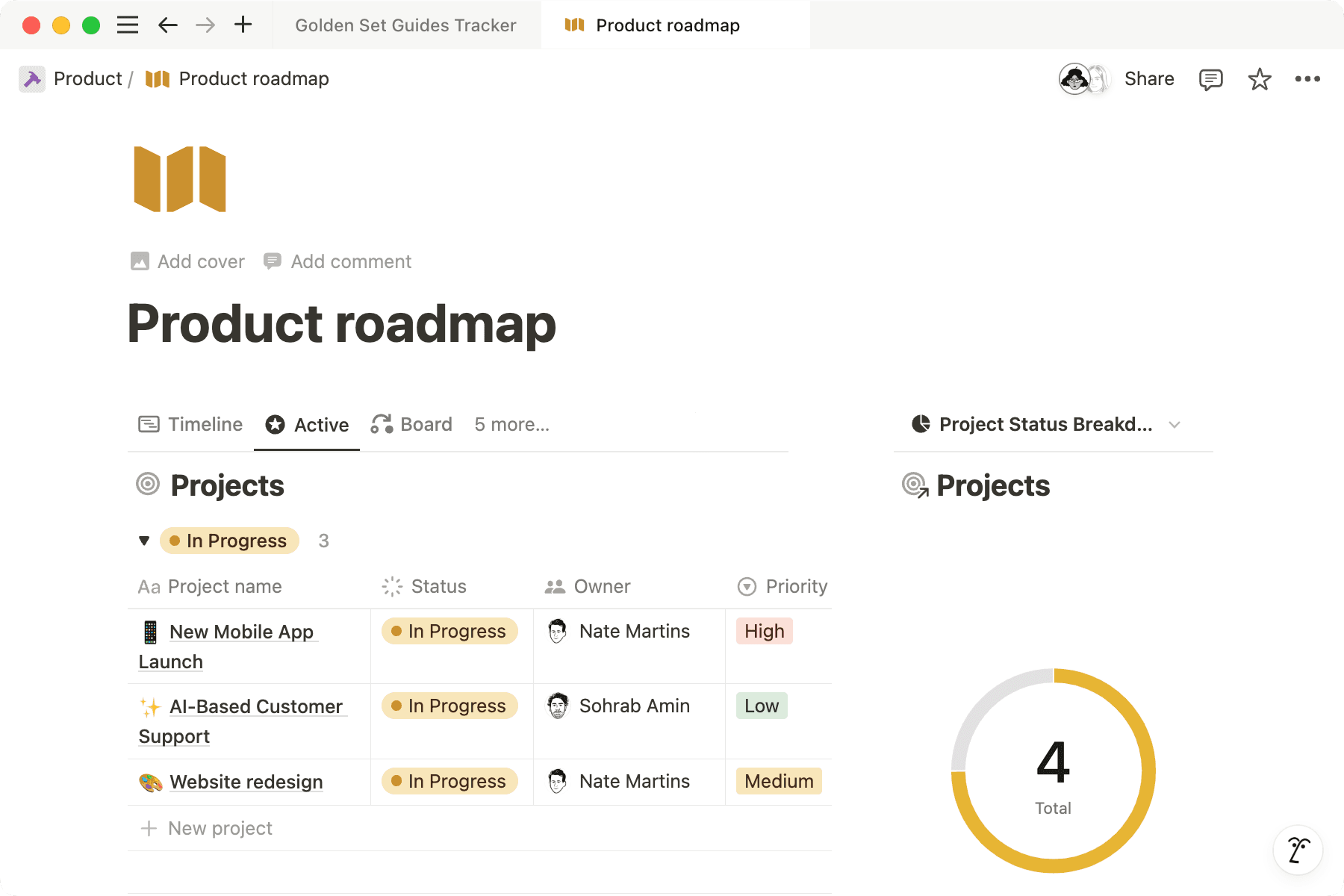
Create a roadmap database
To create your roadmap, add a new page to your workspace and make it a database. Choose a board layout to see all your projects on a Kanban board.
Notion databases allow you to easily organize large sets of information, assign properties to each entry and filter, group, sort, and resurface information in endless useful ways.
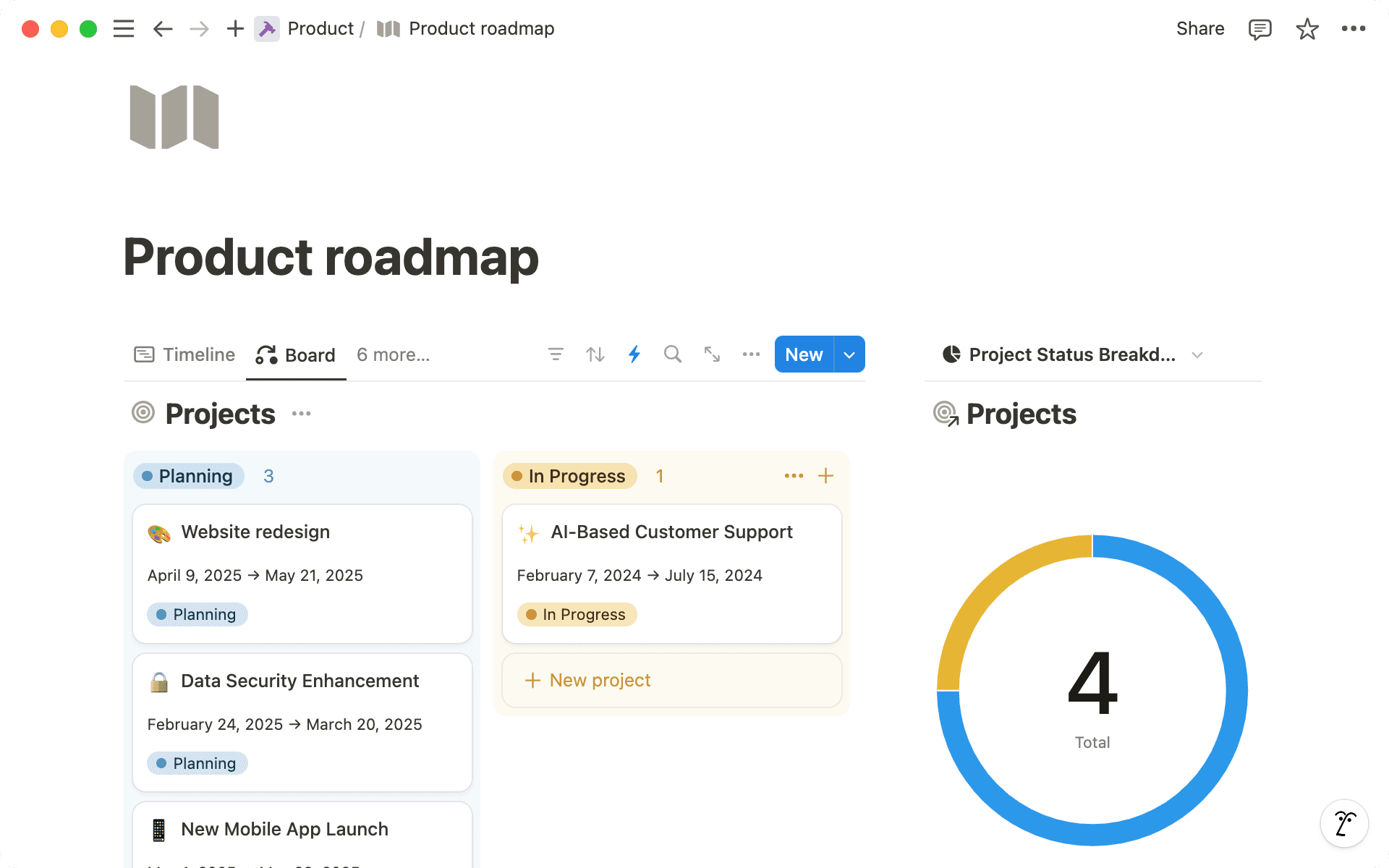
Here are some ways to track and organize projects on your roadmap:
Easily update projects by status — Make sure your database has a Status property so you can mark projects as Up Next, In Progress, Done, etc. Customize the property to add as many steps as you need.
Rank items by priority— Add a select property to create a priority ranking system. Mark projects as P1, P2, etc. Later, you can Sort the database to view high-priority items first.
Add project owners and assignees— The Person property allows you to tag team members as a manager or engineer working on a project. This ensures team members know what they’re responsible for, and you can track what’s on everyone’s plate.
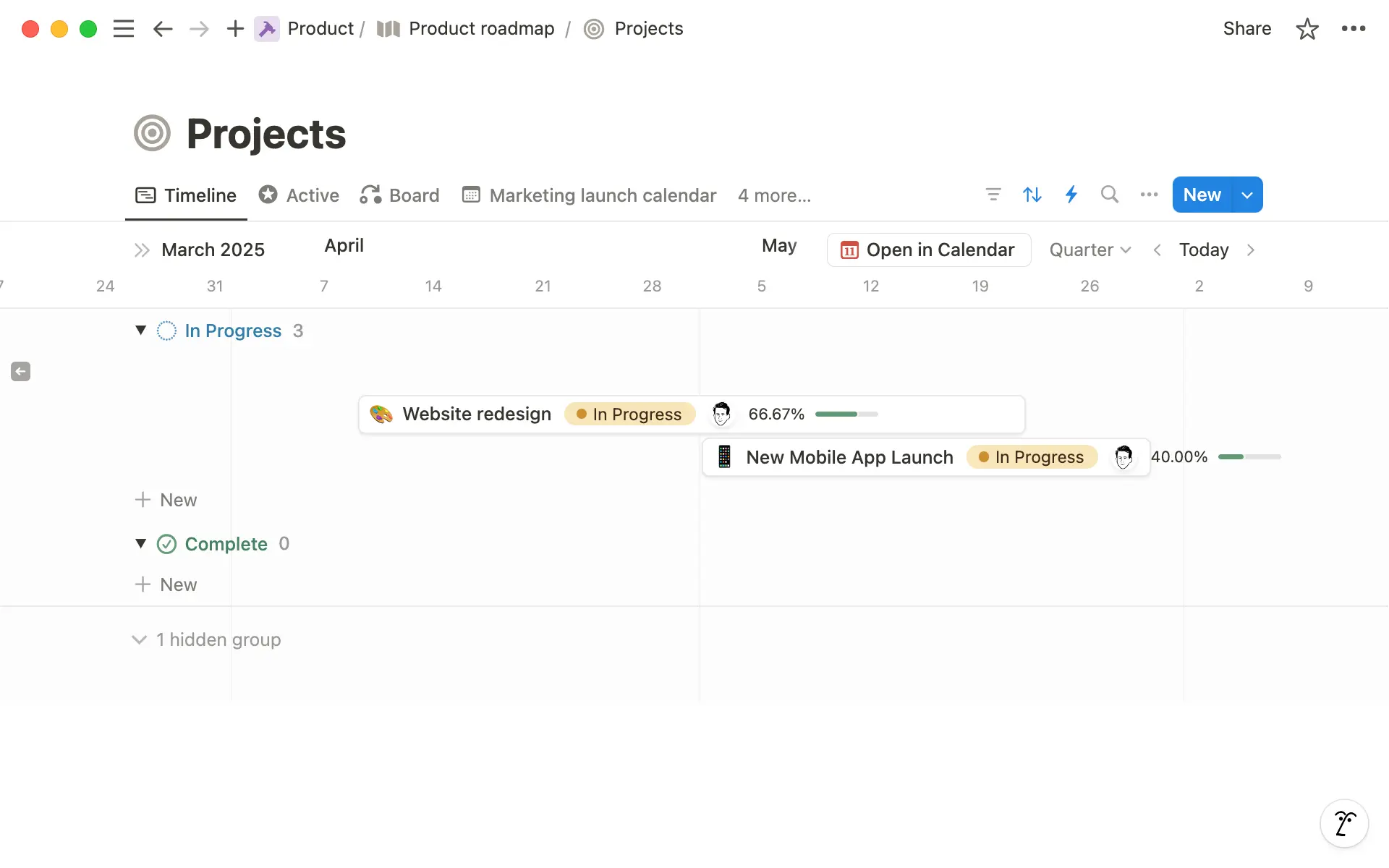
Give projects a timeline— Use the Date property to add start and end dates to your projects. When you do this, you can also view projects on the timeline database layout.
Categorize projects by type — Use the Select property to add different project types to categorize database entries. Tag large initiatives as Epics, and things to fix as Bugs.
View product roadmap in different ways
You can view information in your roadmap in numerous different ways.
Filter to focus on a subset of data— Add one or several filters to your database to focus on a specific range of data. For example, you can filter to show only high-priority projects that are not marked as Done.
Rearrange items in the database— The sort feature allows you to change the order of database items, so you can view projects in order or priority or by start date. You can also Group the content, so, for example, group projects by their project owner to accurately see who’s working on what.
Add different database views— In addition to the Board, there are several more database layout options like Table, List, Gallery, and Calendar. You can add additional views to your database with different layouts. Each view can be filtered, grouped, and sorted differently. This means in one page, you can tab through different database views depending on what you need to see.
Work inside your roadmap
Instead of just linking to other tools, you can get work done in the same place where you track your work, which means less context-switching and scattered information.
Each database entry is a fully customizable Notion page.
Once you’ve added a project to your roadmap and filled up relevant properties, just open the entry to start working right in the page.
You can add any kind of Notion blocks available in the slash / menu - text, checklists, images, video, and embeds from other apps. You can also create sub pages, link to existing pages (such as a Product Requirement Doc), or nest another database in the project page.
To standardize your workflow, add database templates to your Roadmap for different types of projects. For example you can create a Project Spec template for a new project that incorporates the elements you need to scope a new project.
Your roadmap is ideal for bigger projects, but what about the everyday tasks that engineers focus on?
To manage granular work in an engineering task database or scrum board, add another database to manage sprints, assign responsibilities and track issues seamlessly.
Add a Status property, Assignee, and Deadline to your board database. If you want to incorporate sprint tracking, customize your status property to include This Sprint and Next Sprint.
Next, connect this database to your Roadmap via a Relation property. This will allow you to link tasks to the projects they correspond to, making it easier to manage and track work towards completing your projects.
When tracking your tasks in Notion, database automations can speed up your workflows.
For example, you can set up automations for status updates and notifications that can edit properties, create pages, and send updates.
So, you could set up a database automation so that when a task moves to “Completed,” it will update properties on the related Roadmap project, or send notifications to the team’s Slack channel.
Bring work happening elsewhere into Notion
What should you do if your engineers use tools like Jira or Github?
In Notion, work happening in specialist tools doesn’t need to be inaccessible to the rest of your team.
You can bridge the gap by integrating third-party tools, then add Synced database blocks to create a dynamic database that accurately reflects where work is at, and keeps everyone on your team up to date with the latest updates.
Learn more about synced databases.
Having a customer feedback or user research database in Notion can serve a repository for user insights, helping your product team make informed decisions about what to build next.
In your user research database, you can record notes and customer feedback, and categorize insights and customer data with properties.
You can also take advantage of Notion AI in your customer feedback to analyze sentiment, get an overview or summary of each piece of feedback, and even extract potential tasks or fixes that are needed based on what your users say.
In the Properties menu, you will see a section of AI Autofill properties.
Here, you can choose Summary, Translation, or Keywords, or alternatively design your own prompt to generate a response, for example, you could ask it to “Suggest features to build or fix based on this customer feedback”.
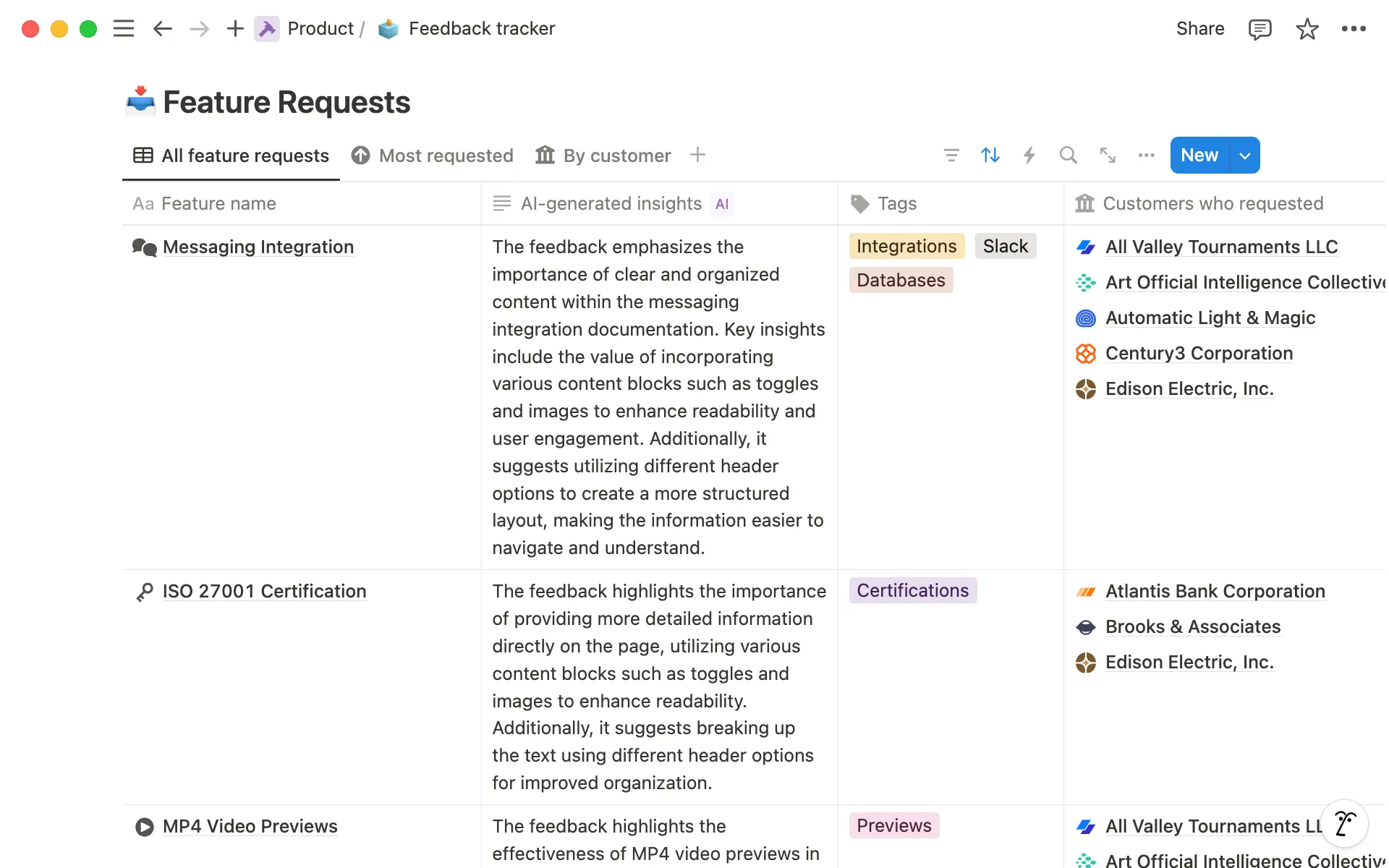
This can help give you an at-a-glance view of what customers are saying, help you generate new feature ideas, and make sure you’re prioritizing the right jobs in your sprint planning sessions.
Connecting feedback directly to product decisions will ensure you’re working on the right projects.
Notion brings all your work into a connected workspace, helping teams stay aligned.
Starting with a Roadmap, you can build your system to include all aspects of work:
Give teams the full context behind their daily work— Link roadmaps and tasks to customer feedback, so team members don’t lose sight of what they’re building. You can outline your product vision on a page to make sure your teams are aligned.
Track customer feedback– Storing user feedback in a Notion database makes it easy to find and act on, ensuring development is driven by customer insights.
Close feedback loops and reduce context switching— Having all aspects of product development from start to finish helps projects stay on track and reduce time wasted switching between apps.
Draft docs more efficiently with templates and AI— You don’t have to start recurring documents like PRDs or tech specs from a blank page every time. Make an outline into a database template, or call up Notion AI to help you draft and edit any kind of document.
Integrate other tools— Notion is an all-in-one tool, but teams who already use specialist tools can integrate their work. From synced databases to embedding Google Docs, Figma files, PDFs, Framer prototypes, Miro boards and more, everyone has full visibility into work happening in other tools.

Get started with a template
설명되지 않은 부분이 있나요?