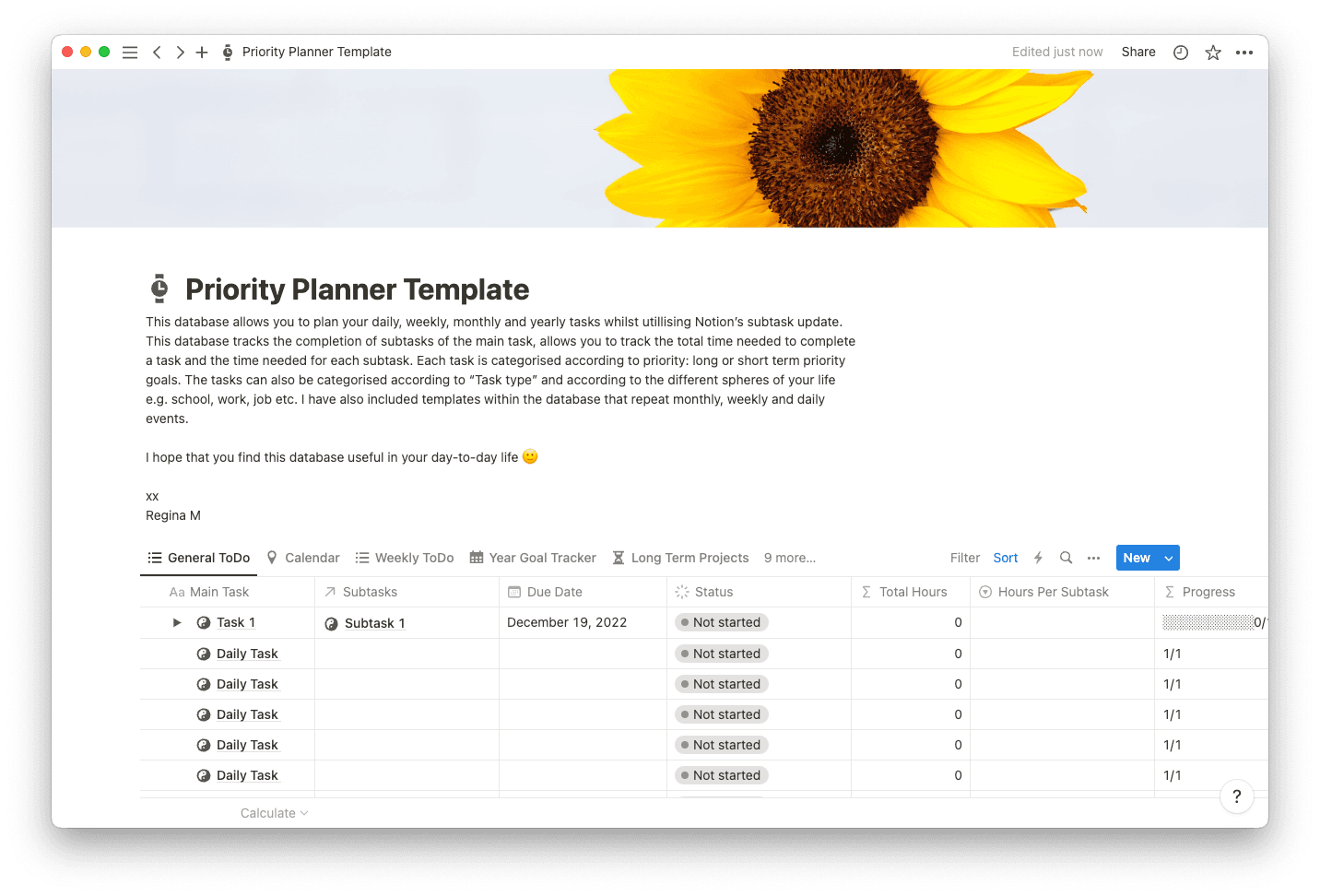
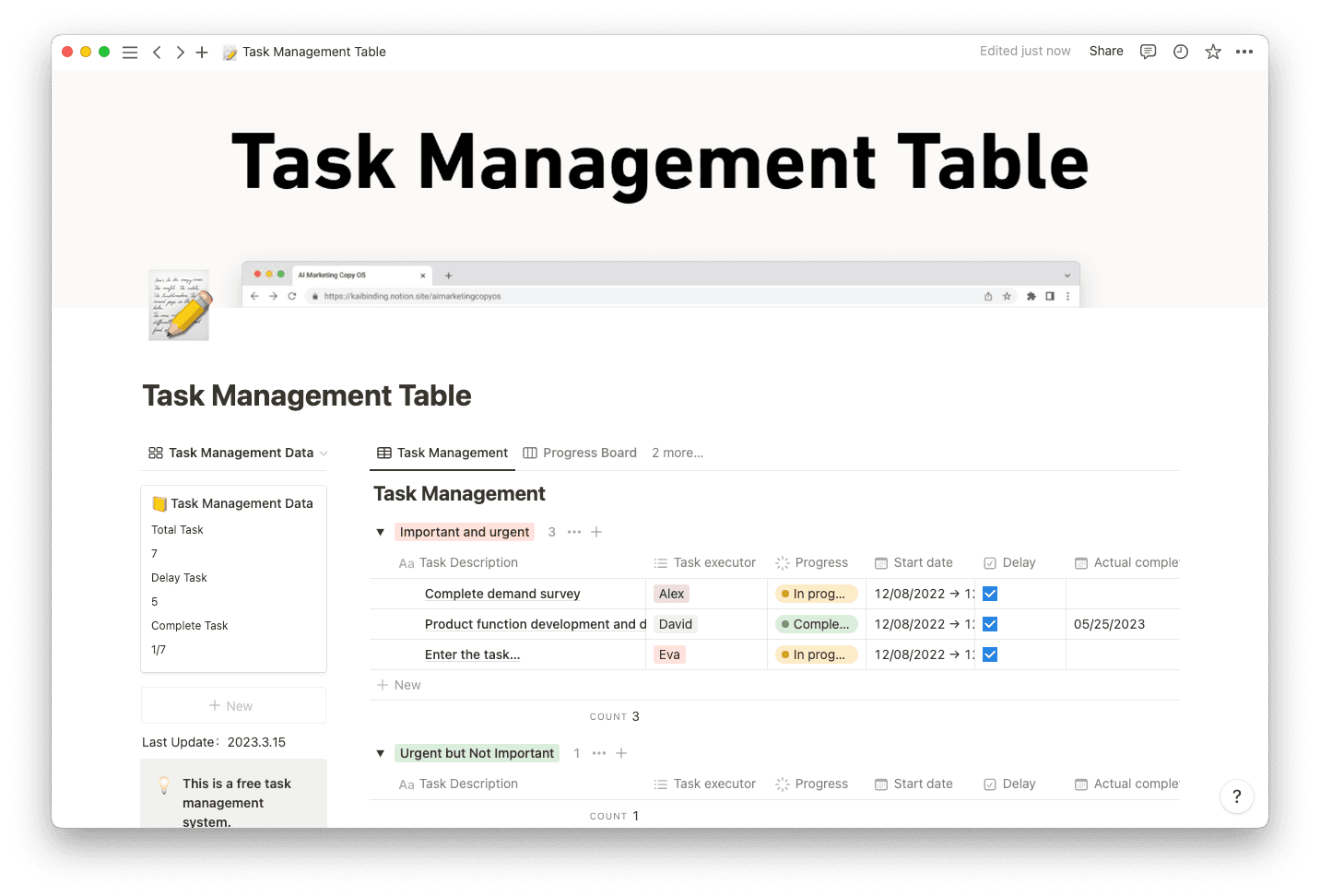
Too often, your list of projects grows faster than your resources to complete them. Those cases call for difficult decision-making about which projects to focus on.
It may be tempting to choose a favorite project. Perhaps one of the jobs is particularly interesting, or another has more promise of success.
To ensure you complete the most worthwhile initiatives, you can implement project portfolio management (PPM), an essential tool for managers juggling multiple projects.
What’s project portfolio management?
PPM is a systematic project-prioritization approach aimed at balancing new with business-as-usual initiatives to encourage growth while optimizing investments.
Leaders use PPM to better understand how projects fit with the company’s long-term goals, considering risks, strategy alignment, and potential return on investment (ROI). More generally, PPM makes an extensive project portfolio more manageable and places the highest-priority items at the top of the to-do list.
The importance of project portfolio management
Organizations use PPM to link strategic objectives to every organization-wide initiative. This practice offers the following benefits:
Strategic alignment — PPM ensures that all projects and initiatives, whether traditional or Agile, align with the organization's strategic objectives. This alignment supports projects that contribute most to the company's long-term goals.
Resource optimization — allocating resources like time, budget, and talent in a structured manner is key. PPM helps reduce resource conflicts between projects, which can improve productivity.
Risk mitigation — PPM allows organizations to assess project risks comprehensively. Identifying potential roadblocks early on enables better risk management and proactive decision-making.
Enhanced decision-making — a successful PPM system provides data-driven insights regarding project performance and ROI.
Improved accountability — PPM fosters a culture of accountability by defining clear project objectives and metrics. Working toward established expectations can motivate team members to perform well and encourage transparency across organizations.
Project portfolio management versus project management
Understanding the distinctions between PPM and traditional project management helps your team determine the best use cases for each strategy.

In short, PPM acts as a guiding structure to help you select and execute the most effective projects. This holistic approach ensures that all projects contribute to the organization's strategic vision. Conversely, project management is a set of best practices for optimal organization and execution of projects. It aligns teams on the best way to accomplish a specific set of tasks.
Industries that benefit from project portfolio management
Here are a few industries that might find PPM especially useful:
Information technology (IT) — PPM can help managers prioritize and manage software development, infrastructure upgrades, and cybersecurity initiatives. The goal of integrating PPM in this space is to ensure that IT investments efficiently deliver maximum value and contribute to organizational objectives.
Project management — project management firms can use PPM to optimize their project delivery processes. This approach helps align projects with their client’s goals and maintain a successful workflow that respects the project’s scope.
Marketing — marketing teams require organized processes and structures when running numerous campaigns and initiatives simultaneously. Managers rely on PPM to keep parallel projects running smoothly. This approach helps them select the most valuable projects, allocate resources effectively, and achieve campaign success. And it ensures that marketing efforts align with the organization's overall strategy.
Construction — the construction industry is growing fast due to increased infrastructure needs across various sectors. With such high demand, construction organizations must optimize resources, reduce costs, and closely monitor projects for timely completion. Skyscraper construction, for example, involves complex, multi-year projects with large teams working in tandem. PPM tools, such as organizational software and portfolio management templates, help streamline workflows across these types of complex endeavors by providing a framework for an organization’s portfolio and easily tracking progress.
Financial services — managing finances, investments, and loans requires a structured and holistic approach. PPM is useful in managing complex projects such as investment accounting, compliance, and risk management. By prioritizing projects and allocating resources strategically, financial institutions can achieve business objectives while meeting regulatory requirements.
The project portfolio management process: 6 steps
PPM hinges on planning, execution, and feedback. Here are six critical steps that structure the process.
1. Initiation
Your organization must define strategic objectives and create a project roadmap that aligns with your goals. This step involves building a PPM team and identifying potential projects. It should serve as a rough outline for what your ideal portfolio looks like.
2. Selection
The selection process involves a rigorous evaluation system to determine which projects are worth investing in. During project selection, analyze each potential project, considering factors such as:
Strategic alignment
Resource availability
Potential ROI
Customer satisfaction
Risk factors
3. Prioritization
Organizations evaluate projects and rank them based on import and impact. This helps in allocating resources to the most critical tasks, with the highest-impact projects that align with strategic goals taking priority.
Common considerations include:
Projects that align with strategic goals should be higher-priority
ROI is generally top of mind for business leaders considering which projects to prioritize
Organizations must determine whether there are enough resources available to complete the required work
Leaders must consider the risks, their probability, and their potential impact
4. Execution
Now, you begin to realize your selected projects. Project teams are responsible for carrying out the work outlined in project plans, relying on prior mapping and prioritization to lend direction and an actionable approach to their work.
5. Monitoring and control
Organizations assess project performance against predefined metrics throughout the project lifecycle, adjusting accordingly to ensure that projects meet their objectives.
One important metric is scope creep, which refers to uncontrolled changes or continuous growth in a project’s scope. Utilizing tools like the Eisenhower to-do list can assist in prioritizing tasks effectively and keeping the range under control.

6. Closure
The goal of the closure phase is to strive for continuous improvement. Upon project closure, teams conduct a thorough evaluation, documenting lessons learned and archiving data for future reference.
The best project portfolio management tools
With multiple factors such as timelines, tasks, and project analyses to keep track of, you’ll need a strong set of tools when taking a PPM approach. Four tools stand out for their ease of use and strong impact.
1. Cost-benefit analysis
A cost-benefit analysis is a fundamental tool in PPM, helping assess the potential ROI of each project in the portfolio. Organizations can prioritize tasks that offer the most significant value by quantifying expected costs and benefits. And this analysis helps decision-makers allocate resources to make the most significant impact.

2. Scoring model
A scoring model is a systematic way to evaluate and rank projects based on custom criteria. Teams assign numerical values to criteria such as customer satisfaction, risk factors, and potential ROI. They then rank projects based on their total scores. This model provides a structured approach to choosing which projects align with the organization's strategic objectives.
3. Objectives matrix
An objectives matrix is a visual representation of how each project contributes to the organization's strategic goals. It maps project objectives against strategic objectives, demonstrating the relationship between individual projects and your organization’s core mission.
4. Decision tree analysis
A decision tree analysis shows all possible outcomes from a decision. This tool lets you map out different choices and their probabilities, costs, and benefits.
This analysis is a great tool when you're struggling to make a difficult choice. It provides a clear, structured way to evaluate various options when the possibilities are overwhelming.
Keep track of all your projects with Notion
With each additional project, your portfolio grows more challenging to manage. Over time, allocating resources can become a crucial project in itself. But you can leverage Notion’s templates, such as the cost-benefit analysis, to assess project feasibility and make informed decisions.
Sign up for Notion today for more ready-to-use templates that help you easily visualize costs, benefits, and potential profits in a user-friendly layout.